︎︎︎ Consumer Behaviour Research on Rainbow Washing
Rainbow washing / Pinkwashing is a strategy that is often implemented by companies to seemingly promote liberalism and democracy through the products or marketing tools using LGBTQ+ symbolism and colors. Companies commonly benefit from this act of marketing, however they are often being accused of not sharing the benefit with the LGBTQ+ community.
Through Q-Methodology, the general opinion on rainbow washing of self-identified LGBTQ+ people is tried to capture to understand til what extend they are aware of it, what the general stance leans towards and how many clusters the opinions form.
Multi-item scale is used, where each Q-Statement is an item to be evaluated by the respondents about their perceptions or thoughts on various aspects of rainbow washing.
Non-probability sampling and snowball technique were employed as it is an exploratory research topic to understand qualitative insights on the topic.
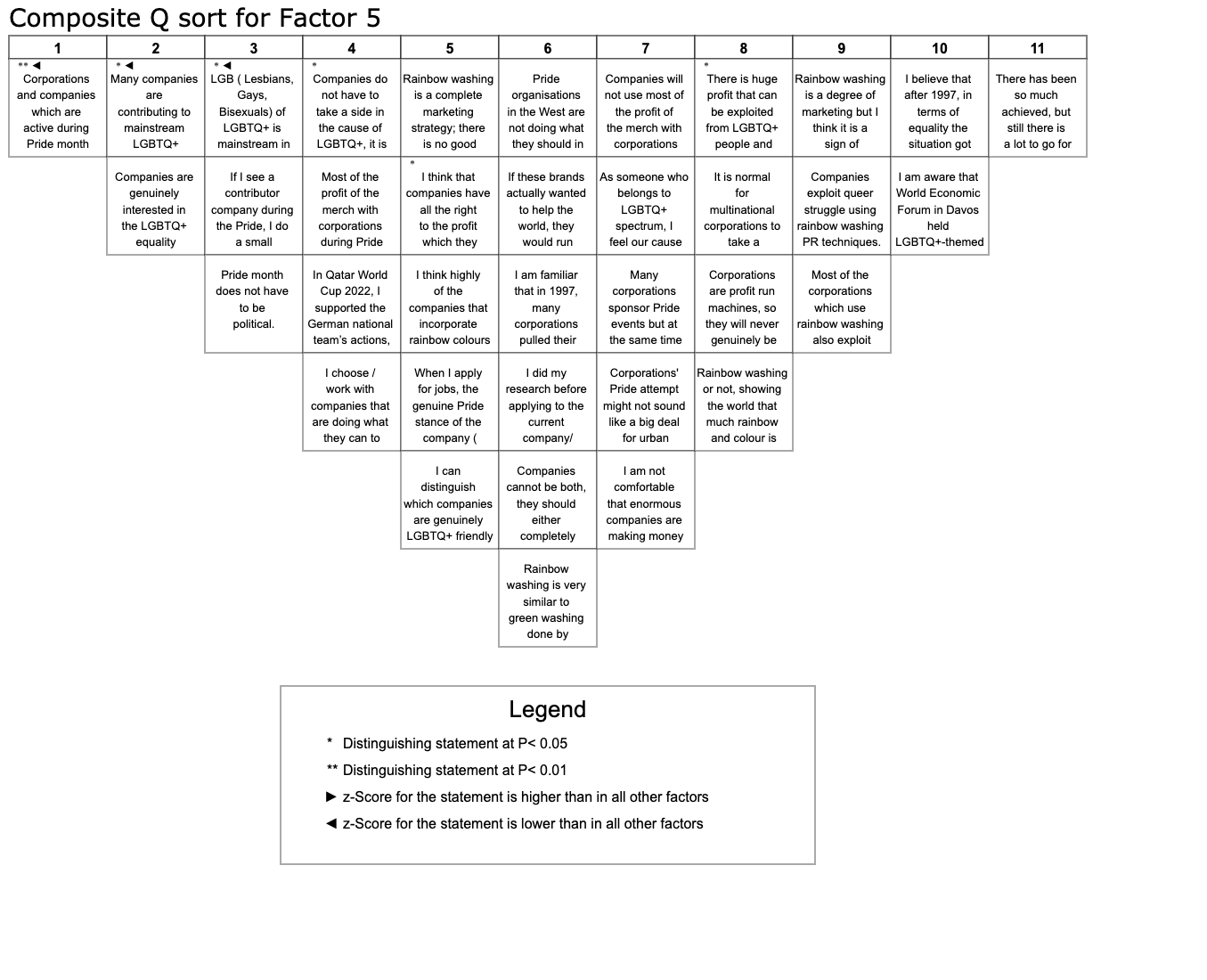
1. Q-Set
Q-Methodology allows us to systematically study the human subjectivity on the topic. Online literature review is used to gather the most common opinions. 36 statements are created from the most common opinions to represent the variety of the thoughts.
2. Q-Sort
Methodology was critical that’s why each participant was interviewed while they were doing the sorting and asked questions related to their preferences. Q-Set consists of 36 statements, and participants are asked to sort them on the table. End data is anonymized.
3. Initial by-person correlation matrix

4. Factor Extraction, Rotation, Estimation & Interpretation

Eigenvalues that are bigger than 1 means meaningful factors and the scree plot gives us at how many factors we use.
Elbow method provides that we use 3 factors.
From the factor analysis we come to the conclusion that the most majority of the people’s opinions are overwhelmingly similar.
Factor analysis and their interpretations give insights on how self-identified LGBTQ+ persons think towards the topic. Qualitative topic is put into quantitative results thanks to factor analysis.
|
Factor |
Perspective |
|
1 |
Corporations should stay neutral in LGBTQ+ issues. |
|
2 |
Rainbow washing is progress, despite its flaws. |
|
3 |
Selective activism (especially against trans people) is a problem. |
|
4 |
Trust in corporate LGBTQ+ support. |
|
5 |
Strategic consumers who research company policies. |
|
6 |
Corporate Pride efforts are better than in the past. |
|
7 |
LGBTQ+ workplace policies matter when choosing jobs. |
|
8 |
Companies exploit diversity for PR. |
|
9 |
Companies should be held accountable for their profits from Pride. |
|
10 |
Corporations should implement real inclusion policies. |
Academic
Dr. agr. Corinna Hempel
Winter 2022
Technische Universität München